Scientific monographs from Polish-Hungarian research published
2023-05-16

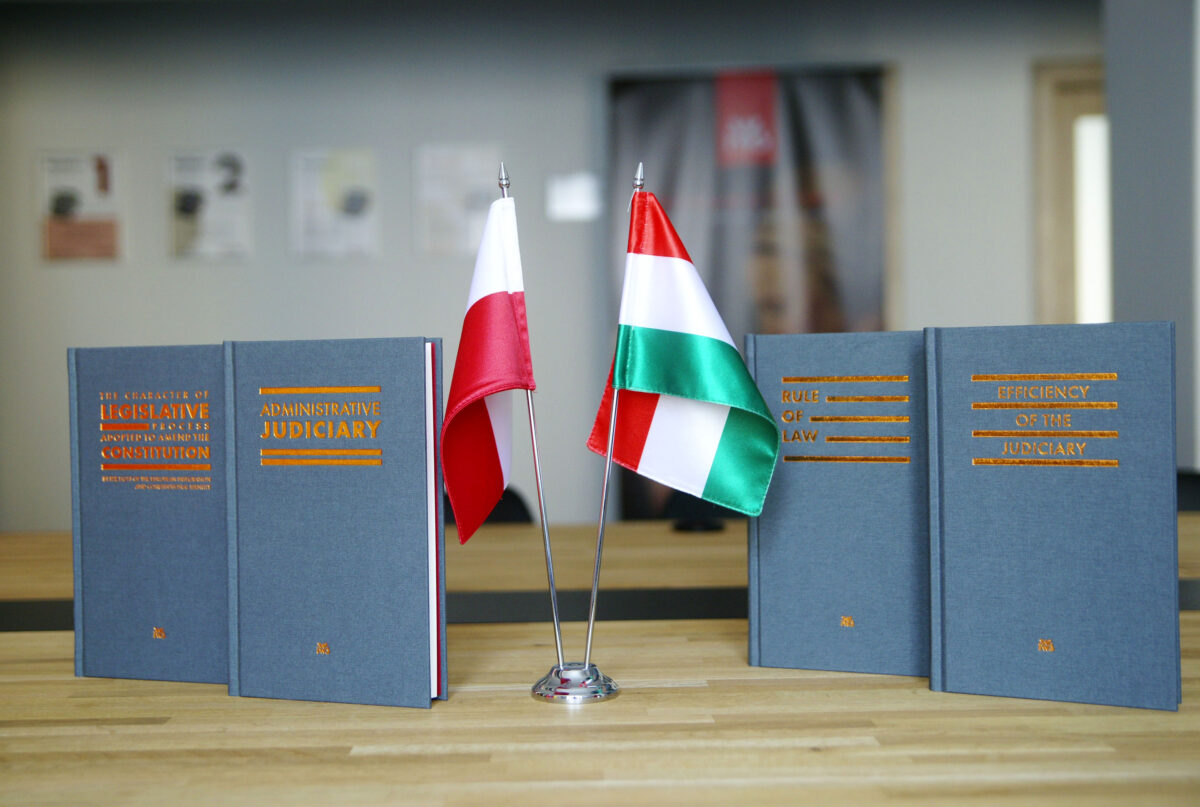
Scientific monographs from Polish-Hungarian research publishedScientific monographs from Polish-Hungarian research publishedThe Publishing House of the Institute of Justice has published four scientific monographs, which are the culmination of the work of the Polish-Hungarian Research Platform 2021. The English-language publications deal with the legislative process of amendments to the Constitution, the rule of law, administrative justice reform and judicial efficiency.
The international research project “Polish-Hungarian Research Platform” is a joint project of the Justice Institute and the Ferenc Mádel Institute of Comparative Law in Budapest. The aim of this project is to revive international cooperation among lawyers and to develop new methods of drafting legislation. The publication of scientific monographs is the culmination of the 2021 international research and a major contribution to the legal debate of a changing Europe. – With our projects in Central Europe, we want to break the monopoly of Western European scientific centers,” points out Prof. Marcin Wielec, the Head of the Justice Institute.
As part of the Polish-Hungarian Research Platform 2021 project, four international research teams were set up to study “the nature of the legislative process for constitutional amendments (in light of European integration and constitutional identity), the rule of law; administrative court reform; and judicial efficiency.”
Administrative Judiciary
The authors of the monograph “Administrative Judiciary. “Administrative Judiciary” point out that effective control of administrative courts is an undeniable and integral element of the constitutional state. In recent decades, both in Hungary and Poland, the administrative judiciary has been under constant pressure for reform, and the structure and mode of administrative proceedings are constantly evolving. Therefore, the goal of the research team for “Administrative Judicial Reform” was to present the current factual state of administrative judiciary in Hungary and Poland with de lege ferenda suggestions for legislators. “The publication is intended to provide assistance and guidance in improving administrative justice in both Poland and Hungary,” – reads the introduction to the monograph, titled. “Administrative Judiciary.”
The monograph features scholarly articles including an analysis of the theoretical and historical aspects of administrative judiciary in Hungary, contemporary challenges to judicial interpretation of administrative law, and a comprehensive overview of the system of legal remedies in the Hungarian Administrative Procedure Code. The publication includes a comprehensive analysis of the issue related to the digitalization of Polish administrative justice, as well as the application of artificial intelligence.
The process of amending the Constitution
The research topic of another Polish-Hungarian team was “characterization of the legislative process for amendments to the Constitution in light of European integration and constitutional identity.” The fruit of this international research is a monograph entitled. ” The Character of Legislative Process Adopted to Amend the Constitution – in the light of the European integration and constitutional identity”.
The publication presents an analysis of the legislative processes in each country to amend the Constitution, through which one can better understand the mechanisms and factors affecting the process of amending the Basic Law in democratic states under the rule of law. The researchers analyze the issue of the impact of the process of European integration on the constitutional system of public power of individual countries. Thus, they consider the relationship between European integration and the sovereignty of member states and the role of their constitutional identity. The monograph also contains an analysis of the directions of changes in the constitutional system and the system of sources of law, i.e. a consideration of the primacy of the constitution and the principle of supremacy of European Union law.

Efficiency of Justice
The subject of the next Polish-Hungarian monograph, entitled. ” Efficiency of the judiciary” is a summary of research on improving the efficiency of the judiciary’s work, its effectiveness, the duration and complexity of cases heard in the courts. “We believe that this publication will provoke a lively discussion in the scientific world and positively influence the practice of individual countries and European institutions,” – The introduction to the publication reads.
The researchers undertook to analyze the effectiveness of the so-called “human factor” in the administration of justice in the context of research on the application of law. Among the numerous de lege ferenda postulates for improving the efficiency of the courts is an indication of greater diligence and predictability in setting dates for procedural actions (hearings, meetings) that take into account the time when the summons can be effectively delivered to the parties and their attorneys.
The publication also offers an analysis of the situation in Poland and Hungary on the right to an effective remedy, which is a key element of compliance with the European Convention on Human Rights (ECHR). Indeed, the right to an effective remedy is one of the most important guarantees within the European human rights system, because it safeguards from national authorities the rights and freedoms that are guaranteed by the ECHR.
Rule of Law
Researchers within the framework of the “Polish-Hungarian Research Platform 2021” have also engaged in the study of the concept of the rule of law, resulting in a monograph entitled “Rule of Law. ” Rule of Law”. “The principle of the rule of law is deeply rooted in European law, its traditions and is considered one of the key achievements of legal thought,” – We read in the introduction of the publication.
The authors of the monograph point out that the rule of law does not have a clearly defined normative boundary, but is only a kind of political philosophy of the so-called functioning of the state’s public authorities, which shows far-reaching flexibility and remains open to new interpretative trends. The principle of the rule of law takes on a diverse content and is characterized by local peculiarities, as a result of the individual legal traditions of each country and its distinct path of historical development. Therefore, any attempt to determine its content requires reference to the peculiarities and nuances operating in the culture and legal system of a particular country. Failure to take these elements into account contributes to controversies and disputes in scientific and political discussions aimed at developing minimum standards of the rule of law.
One of the chapters of the monograph points out that the Court of Justice of the European Union, by giving priority to the criterion of independence over the criterion of legal certainty, including the legal stability of final judgments, contributes to the weakening of the concept of the so-called rule of law in a country and at the same time limits the rights of individuals. In the long run, such a course of CJEU jurisprudence may cause the erosion of the challenged legal system with all the negative social consequences.
The monograph publishes an in-depth analysis of the actions taken by the EU Authorities against Poland in connection with allegations of violation of the rule of law. The meaning of the rule of law in the EU and in Poland, the problem of the relationship between Polish constitutional norms and the norms of EU law, and the limits of permissible EU interference in national decision-making processes and Polish legislation are described.